Levothyroxine and Thyroid Problems: Effects & Alternatives
Levothyroxine is a common medication prescribed for individuals with thyroid disorders, particularly hypothyroidism. It plays a critical role in managing thyroid health by supplementing insufficient hormone levels. While often effective, it's crucial for patients to be aware of its side effects and explore potential alternatives where appropriate.

Levothyroxine is typically prescribed for individuals suffering from an underactive thyroid, or hypothyroidism. This condition occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone, leading to symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and depression. The medication helps normalize hormone levels, improving overall symptoms and quality of life for many patients.
Who Needs Levothyroxine?
Levothyroxine is recommended for individuals diagnosed with hypothyroidism, which may result from Hashimoto's disease, thyroid surgery, or radiation therapy. It is crucial for those experiencing significant symptoms impacting their daily life. Regular blood tests are necessary to tailor the dosage to individual needs, ensuring effective treatment outcomes.
Dosage and Administration
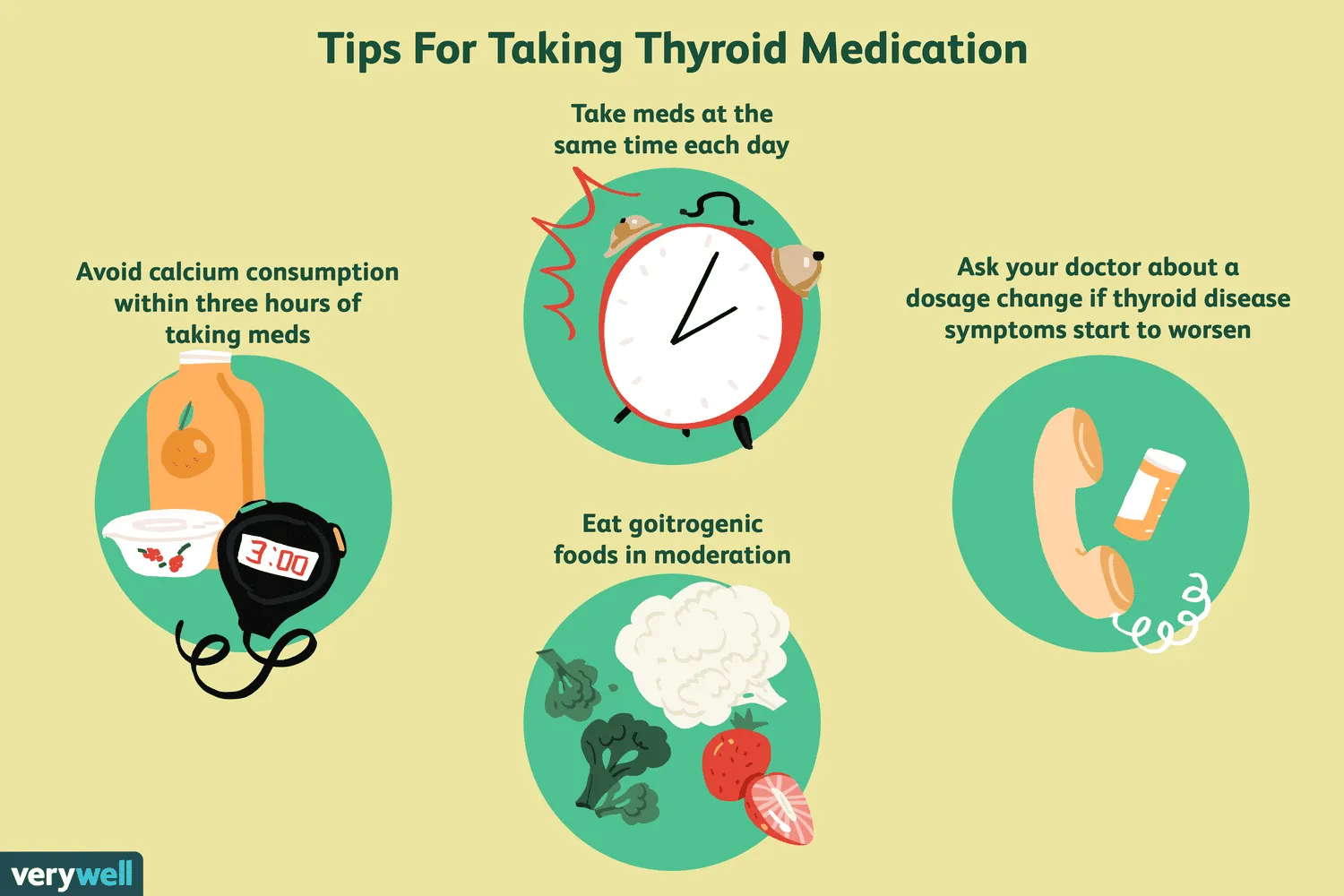
The dosage of levothyroxine varies based on factors like age, weight, and severity of hormone deficiency. It is typically taken orally, once a day on an empty stomach, to maximize absorption. Healthcare providers frequently adjust doses based on thyroid hormone levels and patient response, emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring.
Side Effects and Precautions
Common side effects of levothyroxine include headaches, sleep disturbances, and changes in appetite. In some cases, patients may experience palpitations or nervousness. It's important to communicate with healthcare providers about any adverse effects encountered to adjust treatment as needed. Patients should also discuss any other medications or supplements they are taking to prevent interactions.
Long-Term Effects and Monitoring
Long-term use of levothyroxine requires ongoing monitoring to ensure optimal thyroid hormone levels and prevent potential complications such as osteoporosis. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to adjust the dosage as necessary and address any emerging concerns. Patients should be informed about the importance of compliance and maintaining a consistent routine.
Alternatives to Levothyroxine
For some patients, alternative treatments might be considered if levothyroxine is not well-tolerated or effective. Natural desiccated thyroid and combination therapies are potential options. However, these alternatives should only be pursued under careful medical supervision. Lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and supplements may also support thyroid function, complementing medication when necessary.
Related Issues
What Are The Long-Term Harms of Levothyroxine?
Thyroid disorders affect millions worldwide, with hypothyroidism being one of the most common endocrine conditions. Levothyroxine, a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine, is the primary treatment for underactive thyroid. While highly effective, it requires careful management and adherence to specific precautions. This article delves into the essential considerations for levothyroxine use, empowering patients to optimize their thyroid treatment.
Migraine Massage: Benefits, Techniques And Tips
Migraines are a debilitating form of headache that can significantly impact a person's daily life. They often come with severe pain, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound. Many people turn to alternative therapies like massage for relief.
Weight Loss Injections: A New Option for Shedding Pounds
With the increasing prevalence of obesity worldwide, many individuals are seeking effective ways to lose weight. One popular option that has gained attention is weight loss injections. These injections use specific medications or compounds to regulate metabolism, control appetite, or break down fat, helping people achieve their weight management goals. This article will cover common types of weight loss injections, how they work, their benefits, and where to find such services.